You can enable retention for most Microsoft 365 applications and their data types. Once a retention policy is on, it makes sure that the existing items (at the moment when the retention policy is created) and all new data remain in Microsoft 365 for a prescribed period of time.
If users or admins delete data, the retention policy will remove it from Microsoft 365 applications, but the items will still be accessible & searchable using Compliance eDiscovery and in the Preservation library.
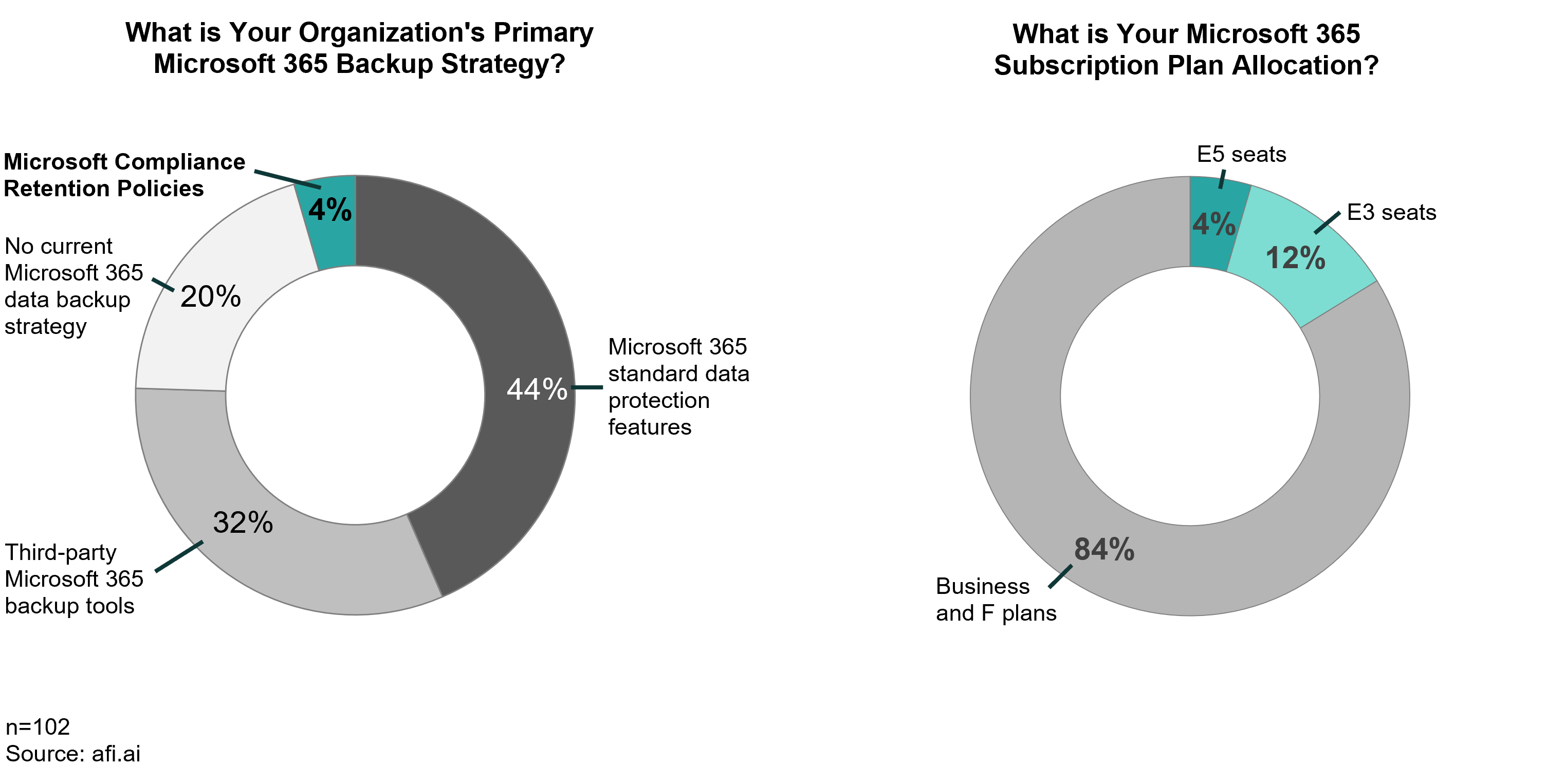
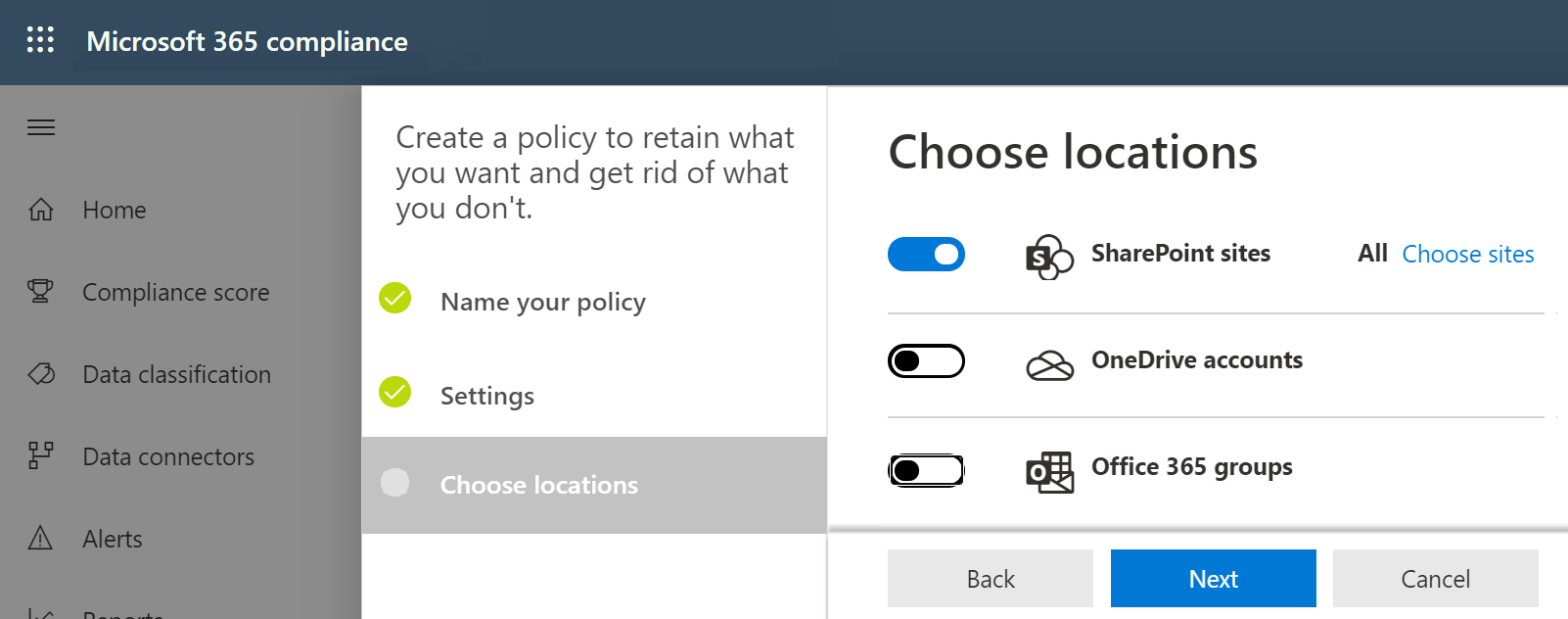
The scope of Microsoft 365 retention policies
SharePoint and OneDrive
- Versions are retained for libraries where it's enabled
- Folder structures can be recovered from eDiscovery
- Site looks/themes and related settings not retained
- SharePoint membership permissions are not preserved
- Sharing and access permissions aren't preserved
Exchange Online
- Messages (drafts, in-place archive) & attachments retained
- Entire mailbox (sub)folder structure is preserved
- Teams messages captured sent by user are retained
- Site looks/themes and related settings not retained
- Calendar items and tasks with no end date are not retained
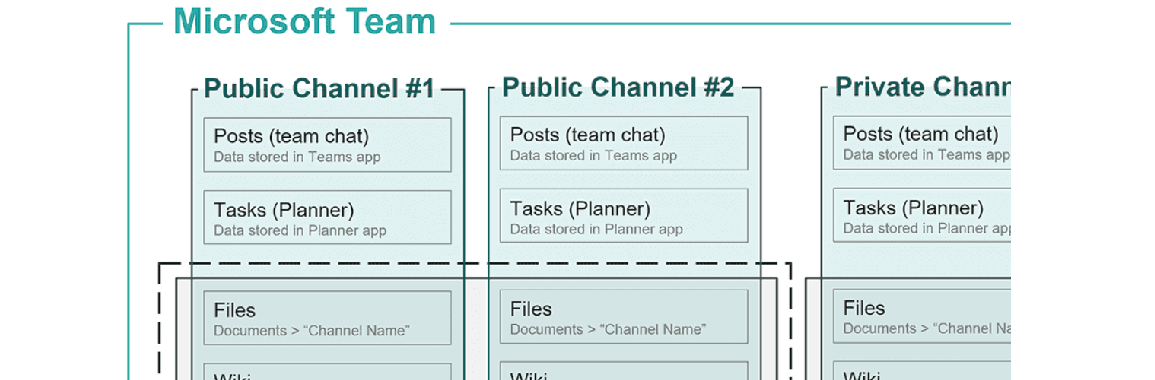
Teams
- Chats and channel (private/public) messages are retained
- Message attachments aren't retained by default (you need to separately enable retention for SharePoint & user OneDrives)
Groups & other
You can enable retention policies for MS Groups, but they'll only retain SharePoint data linked to the groups. No user membership, permissions & other metadata is backed up by retention policies.
Exchange Online
The retention policies preserve all email messages, including unsent drafts, messages moved to the trash bin, messages stored in the Archived folder as well as in the in-place archive.
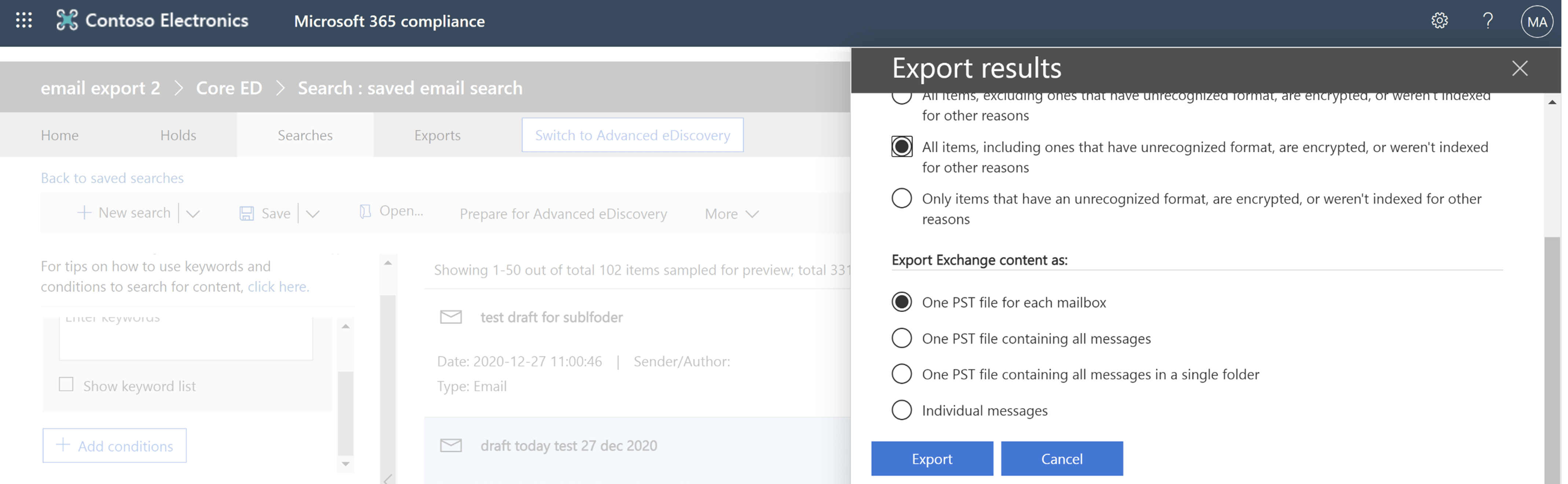
Exchange data can be exported in a PST file or a set of individual messages using the eDiscovery admin interface. Administrators with eDiscovery permissions can also access deleted messages in Recoverable Items Exchange folder.
Exchange Online eDiscovery export options
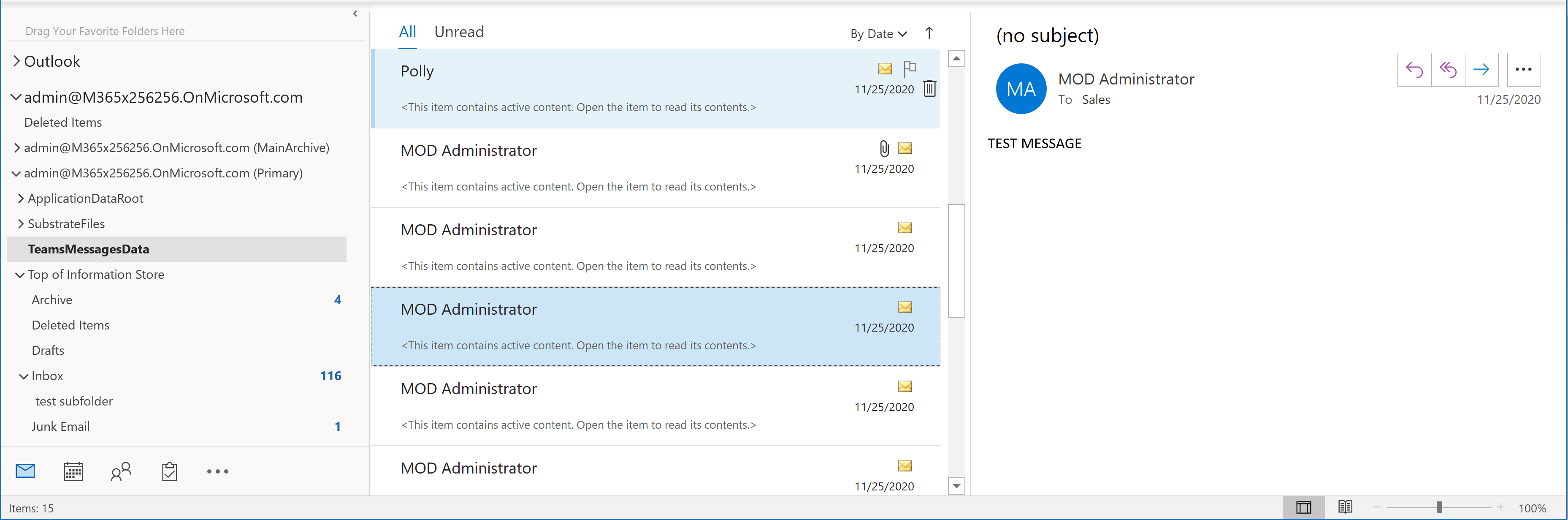
Although Microsoft recommends enabling a separate retention policy to capture Teams data, the policy we enabled for Exchange mailboxes also captured a system folder TeamsMessagesData with all Teams channel and individual messages that the Exchange users sent (though not the messages they received).
Exchange Online eDiscovery PST export (TeamsMessagesData captures Teams messages).
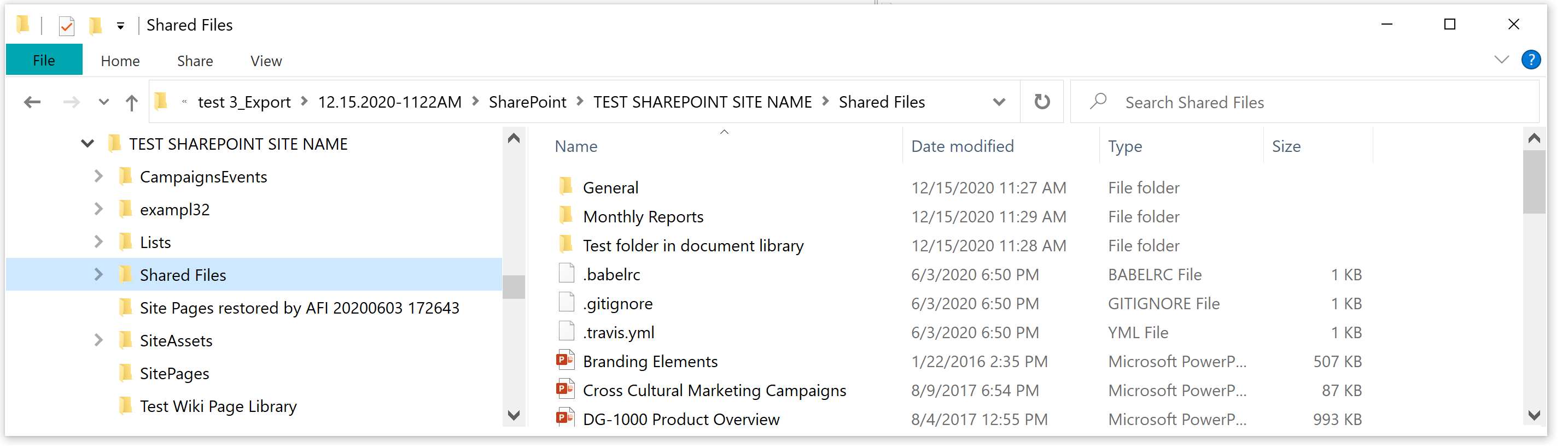
SharePoint Online and OneDrive
Compliance retention helps retain files and list items and their versions. The versions are retained only if the versioning is enabled for the library/OneDrive.
The items can be exported offline in their original folder structure. If there is more than one version of a file (list), all of them will be exported (old versions will have "_vX" added to them where X is the version number).
SharePoint online export folder.
How Standard Versioning Works With Retention
Retention policies are often described to retain all document/item versions created, but this is not 100% correct.
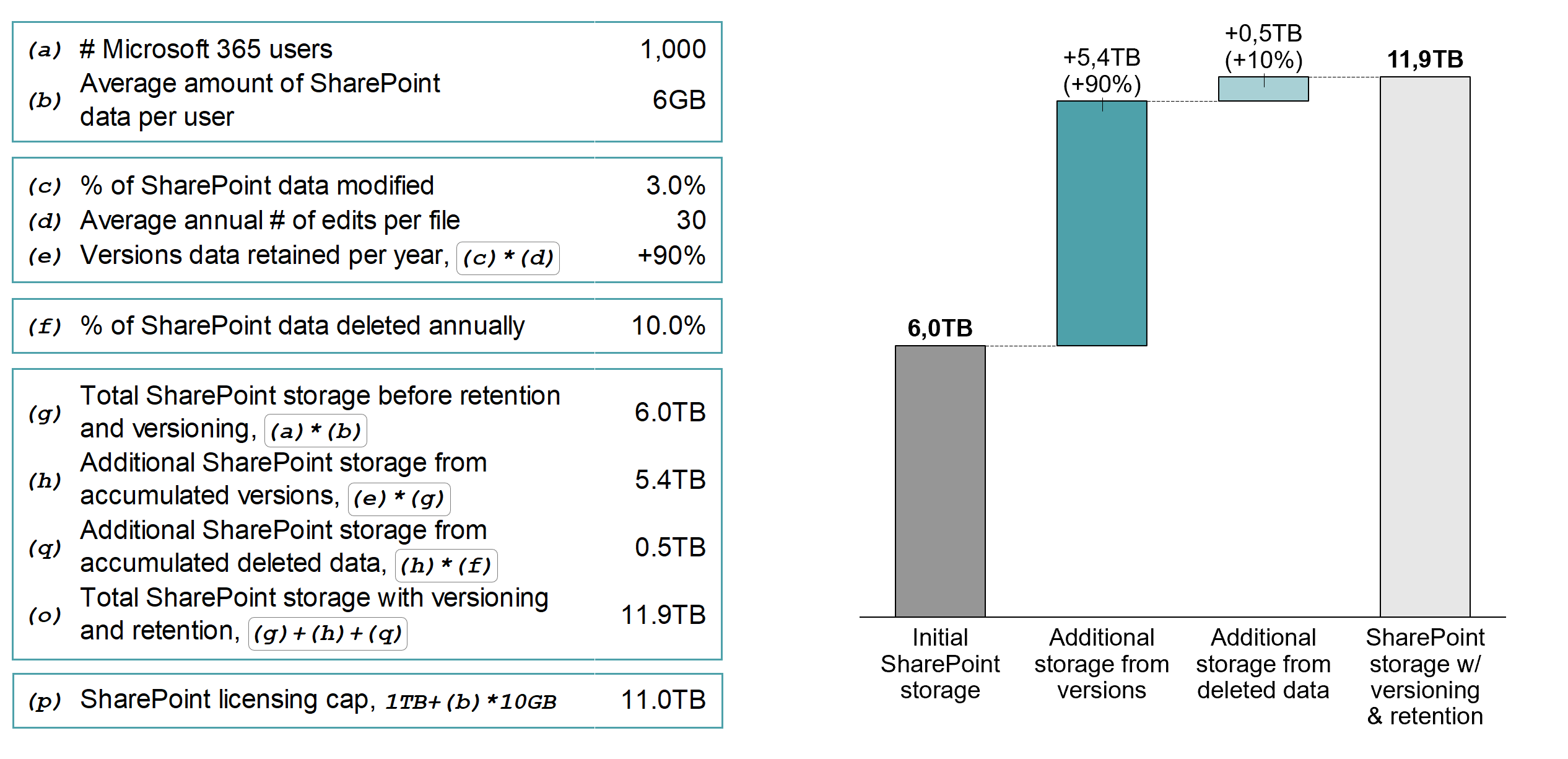
The retention policies rely on the standard SharePoint & OneDrive versioning mechanism to retain versions. Retention policies retain versions only if the standard versioning is enabled. By default, the versioning is turned on for Document Libraries and OneDrives and the number of retained versions is set to 500. No versions are retained for other data types (lists, web pages, etc) by default.
The standard versioning is available in all Microsoft 365 plans, but when it is used without the retention policies it is significantly limited by the fact that users can accidentally or intentionally delete file versions. When you enable the compliance retention you overcome this limitation as Microsoft 365 will not allow to delete versions while a relevant retention policy is on for the data (see Deletion flow for details on what happens to versions if you delete an entire file).
You can disable or enable versioning for each document library and list (one by one) when you create it or later. The settings allow to retain up to 50,000 versions for documents and lists. Admins can also disable versioning entirely (this is the default setting for lists).