The standard post-deletion retention is a mechanism that keeps deleted items and entire SharePoint sites for some time (up to 107 days) before deleting them irrversably. This enables Microsoft 365 administrators to recover items within the retention window.
First-stage recycle bin
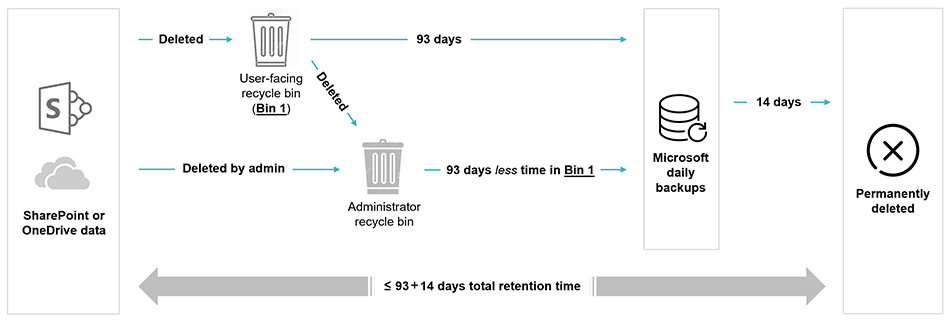
When users delete items from SharePoint sites, the data is moved to the first-stage recycle bin (=user facing recycle bin, or site Recycle Bin). It is kept there for 93 days (unless it is deleted from the bin earlier).
After 93 days the data is removed from the recycle bin, however it still remains in Microsoft daily backups for additional 14 days.
SharePoint online retains data for up to 107 days after it is deleted
Second-stage recycle bin
If users delete data from the first-stage recycle bin, or if SharePoint site collection administrators delete data from a SharePoint site, then the data is moved to the second-stage recycle bin (=administrator Recycle Bin, or collection Recycle Bin).
When an entire site is deleted, it goes straight to the second stage recycle bin.
Only SharePoint site collection administrators can view and recover data from the second-stage recycle bin. Data is kept there for 93 days less the amount of time the data was kept in the first-stage recycle bin.
For example:
- a document library file is deleted by a user (so it's moved to the first-stage recycle bin)
- it is then deleted from the (first-stage) recycle bin
- it'll therefore go to the second-stage recycle bin and will spend there 63 days (unless an admin deletes it from there earlier).
After data is deleted from the second-stage recycle bin it remains in Microsoft daily backups for additional 14 days.
Microsoft backups
Daily Microsoft SharePoint backups provide 14 days additional days during which you can recover deleted data. Administrators can contact Microsfot support to recover the data during this period. Only full SharePoint site recovery is available (no item-level recovery).
You will need to specify the date you want to recover the data from, but there is not way to recover specific versions, or use a recovery point from a specific time.
The post-deletion retention settings cannot be changed or configured and they are the same for all Microsoft 365 plans.
Data within subsites follows a similar retention & versioning cadence as documents, lists and pages in the “parent” site.
Check Microsoft documentation to learn more about standard SharePoint retention & recovery.